Stomach Acid Is Good For You
The many dangers of acid blocking medications
Story at a Glance:
•Many pharmaceuticals on the market are automatically given to large numbers of patients despite the harms of these medications often greatly outweighing their benefits.
•One of the worst offenders are the acid suppressing medications, and their overprescription goes hand in hand with a widespread medical blindness to the critical functions of hydrochloric acid throughout the body and the actual causes of acid reflux.
•A variety of safe and non-invasive approaches exist to address the wide range of (often unrecognized) complications from acid reflux and dysfunctional stomach acid production.
Note: this article is a bit on the longer end, but since the stomach acid issues profoundly affect so many people, I felt this article needed to be able to cover all the key points.
One of the more depressing parts of being an awake physician in the medical system is reading the drug lists of the patients you see and realizing how many prescriptions they are on that do not benefit them, and in many cases harm them. Presently, 66 percent of U.S. adults are estimated to have at least one prescription and on average, they have 9 prescriptions filled per year (which can include renewals of an existing one).
Since doctors are extremely reluctant to terminate existing prescriptions, this creates a scenario where people get placed on more and more drugs as they age (some of which are for treating the side effects of other drugs they are taking).
This situation is even worse for the elderly, who both have more time to be put on an increasing number of medication and due to their altered physiology are also the most vulnerable to the harmful effects of those mediations. For example, from 2009-2016, after 2 billions office visits were assessed, it was found that for adults over 65, 65.1% were on two or more drugs, 48.9% were on four or more, and 36.8% were on more than five (with the highest use occurring in the oldest Americans).
One of the best illustrations of the problem came from a study that compared 119 disabled elderly adults living in nursing homes to 71 matching controls. These patients (who on average were on 7.09 medications) were screened for which of their medications clearlymet the existing criteria for being discontinued (on average 2.8 per patient). After those medications were discontinued in the test group, when compared to the controls who remained on all of their existing prescriptions it was found that:
•The death rate dropped by 23% (in one year, 45% of the control group died whereas 21% of the test subjects died).
•The annual rate of hospital referrals dropped by 18.2% (30% of the controls vs. 11.8% of the study).
•Not surprisingly, there were also significant cost savings from withdrawing the unneeded medications.
In short, doing nothing except terminating some of the most egregious prescriptions for our elders (who often lack the autonomy to refuse their prescriptions) resulted in a 23% reduction in their death rate. When you consider that many of these drugs are approved for much smaller reductions of the death rate, and that they frequently have a variety of other concerning side effects (e.g., triggering dementia), the absurdity of this situation (e.g., that this pivotal study never changed how we practice medicine) becomes clear.
For example, almost everyone is put on statins—especially as they get older, yet in trials evaluating statins, for instance to evaluate their effect on 50-75 year old patients’ risk of heart disease, statins caused a 0.4% reduction in the annual risk of a major cardiovascular event (most of which are not fatal) and no benefit in the overall death rate. Likewise, according to the existing trials (which are almost certainly biased to favor the pharmaceutical companies funding them), it was found on average that taking a statin for five years would increase your expected lifespan by three days. In contrast, statins are notorious for causing adverse effects which affect at least 20% of recipients. These effects include cognitive impairment and dementia, personality changes, loss of sensation throughout the body and significant muscle weakness or muscle aches.
This seems absurd until you also consider that statins are also one of the most profitable drug markets in existence.
Note: a more detailed summary of the tragic adverse effects of statins can be found here.
The Worst Drugs on The Market
A frequent question I receive is what the most harmful medications in America are. Prior to the COVID-19 vaccines (which I feel have earned that distinction) there in turn were two ways I interpreted that question.
Which medications are frequently prescribed to everyone, often provide minimal benefit, and cause real harms you frequently seen in practice?
Which medications are highly toxic and have more narrow uses, but are nonetheless frequently given to patients in many cases where the harms of doing so far exceed any possible benefit.
In regards to the first interpretation, almost every integrative physician I’ve ever asked for their top 5 has listed the following:
•Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs—the focus of this article)
•SSRI antidepressants (e.g., Prozac)
•Statins
•NSAIDs (e.g., Ibuprofen)
•Birth control pills.
Note: some have also argued tylenol, benzodiazapines (e.g., valium) and flu shots also belong on the above list. Likewise, opioids used to always be on it, but now that the government has gone in the opposite direction and curtailed their prescribing, so they are no longer widely distributed and hence no longer can be in the first category.
In regards to the second interpretation, there are many more answers, but some of the most common ones include:
•Anti-psychotic meditations (used for a wide variety of mood disorders)
•Accutane (used for acne)
•Ciprofloxacin and other fluoroquinolone antibiotics
•Finasteride (commonly used for hair loss)
•Gadolinium (this is used as a contrast agent for MRIs)
•Gardasil (the HPV vaccine)
•Lupron (which amongst other things is used as a puberty blocker)
In sales, a common practice is to start with a free or low cost item, and then from the pool of people who get it, use their investment to sell them a moderately priced item, and then from the pool of those buyers, sell a more expensive item and so forth. This business practice, in turn, is known as creating “sales funnels.”
Frequently, with the above drugs, I see a variety of sales funnels. For instance, adolescent girls are frequently put onto birth control pills by their pediatricians (e.g., this survey found 54% of women aged 15-19 had used the pill)—often for reasons unrelated to sex (e.g., painful periods or PMS in a twelve year old).
Birth control pills in turn frequently cause significant mood swings and mood alterations (e.g., a large study detected a 130% increase in the rates of depression during the first two years of using the pill), which often leads to these new mood disorders being “treated” with an SSRI antidepressant (which now more than 10% of teenage girls are on). In turn, one of the more common side effects of SSRIs are other new psychiatric disorders (bipolar I is the most common) which are then treated with an antipsychotic (or another mood stabilizer).
As a result, I often meet young women who went through this sales funnel in their adolescent years and now are on the fairly damaging anti-psychotics. Additionally, I’ve also spoken to a few people who had been on this pipeline and said the neuropsychiatric damage they developed from the HPV vaccine was ultimately tipped them over the edge (which then required taking an antipsychotic which frequently caused even more chronic psychiatric and neurological issues for them).
As you might guess, I am not a fan of this business model, and one of my goals here is to gradually go through why each of these drugs cause so many problems.
Translational Medicine
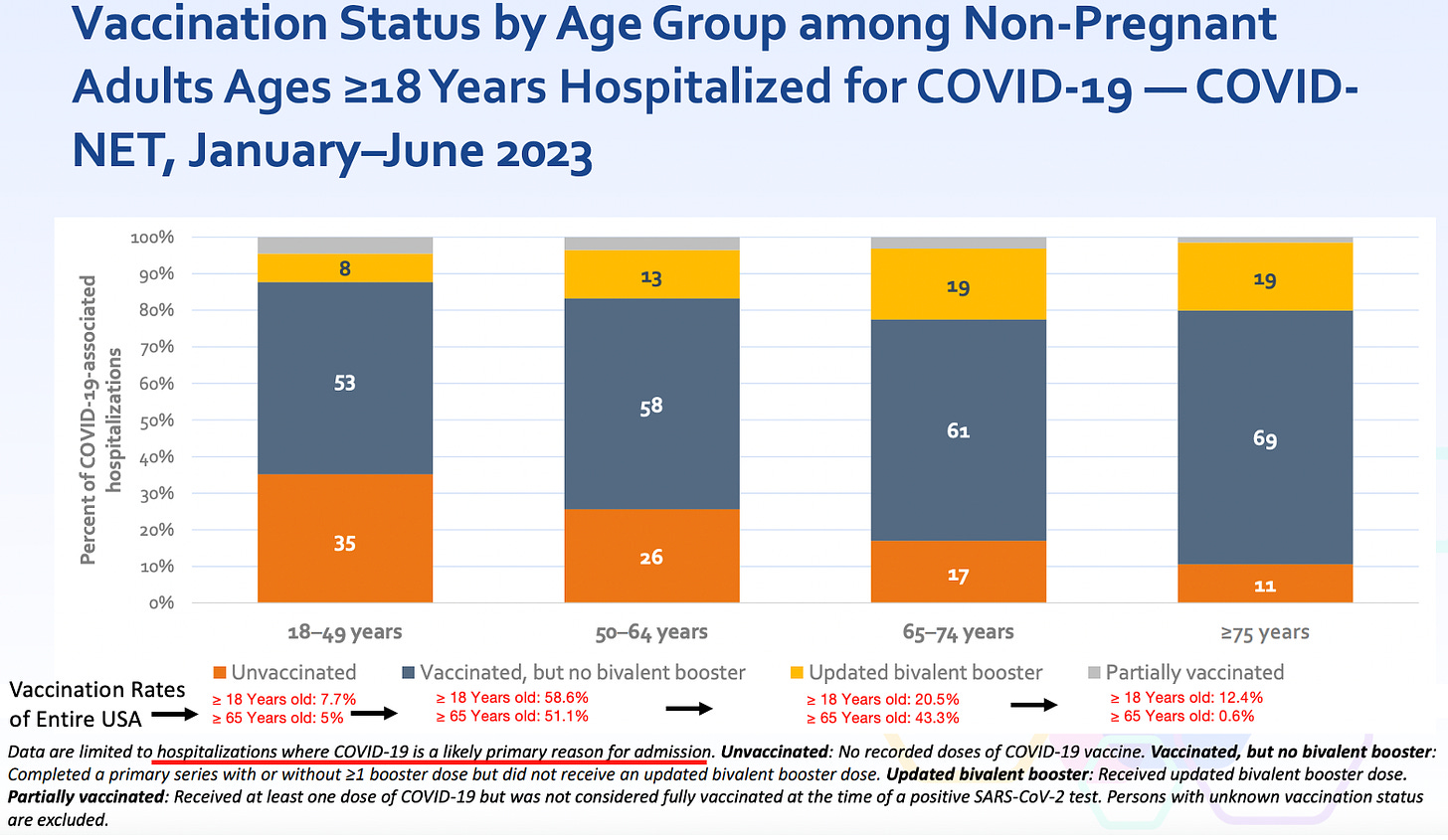
Since medicine is supposed to be “science based,” a recurring question is why the most important scientific discoveries are never adopted into clinical practice, or if they are, often take years if not decades to be (this is what the discipline of translational medicine seeks to address). This for instance has been shown with the COVID-19 vaccines, as over and over, the evidence demonstrated they were neither safe nor effective, but nonetheless every clinical guideline keeps on recommending their use on everyone. For instance, consider how effective the vaccines are per the CDC’s own recent admission:
Note: the population vaccination percentages were sourced from this CDC dataset, which I believe likely overestimates how many people were vaccinated, as at least 25% of the people I know never received the vaccine, whereas the CDC claims only 7.7% didn’t.
If you look at the above data, it’s clear this vaccine is not an effective product, and once the harms of the vaccine are also taken into consideration, especially given how vocally opposed the public is to those products, it becomes very difficult to justify continuing to use them. Nonetheless, the FDA is still rubber stamping the newest COVID vaccines (with virtually no data to base the approval upon) and hospital systems are beginning to mandate the new booster for their employees. I believe all of this helps to illustrate how resistant the medical field is to acknowledging data which challenges existing beliefs.
Note: I always believed the COVID-19 business model was to saturate one market at a time and then pivot to the next one once the previous was saturated. This for example is why we saw a successively more aggressive series of pushes to sell the vaccines (e.g., first selling them through a scarcity model, then with financial incentives, then soft mandates, and then eventually hard mandates) or why the vaccines were pushed onto children (who have no risk of dying for COVID-19) once adults no longer were willing to receive more of the vaccines. Likewise, I previously argued that once no more of the initial two-shot series could be sold that they would pivot to acknowledging it didn’t work (e.g., see this recent announcement by the governor of New York) so that the boosters which “did work” could next be sold to the public.
When I first started my medical education, a mentor told me:
The medical profession has always been remarkably conservative in adopting new ideas. Try not to get frustrated if they won’t consider the evidence you present to them.
In turn, on this Substack, I’ve tried to gradually review examples of the widespread refusal of the medical profession to consider critically important evidence that was being presented to them. By doing so, I’ve hoped to show how this behavior is the norm rather than the exception, so each of you better understand why there has been such a steadfast rejection of the science throughout the pandemic.
For example, I am a long time fan of Dr. Mercola (I’ve read his website for decades). A major reason I’ve read it has been because Mercola has repeatedly presented ideas (with compelling science to support them) about medicine and health the medical community rejected, and over and over I’ve seen those ideas be accepted as self-evident truths years later by my profession (e.g., Dr. Mercola correctly predicted that Vioxx would be a disaster).
The reason I mention all of this is because despite Mercola having the most read natural health website in the world (leading to many patients demanding what he puts forward and many physicians adopting his advice), alongside Mercola’s ability to clearly prove his ideas with existing science, the medical profession still has taken years if not decades to accept those ideas. Mercola’s example hence serves to illustrate just how powerful the barriers to translational medicine are.
Another pioneer in the integrative medicine field is Jonathan Wright MD, and much of the initial knowledge base of integrative medicine came from his pioneering work, particularly his research (he had a knack for digging up forgotten research that was extremely relevant to patient care). In this article I plan to review many ideas I was initially exposed to by Wright, and many parts of this article (e.g., the quotations) are summaries sourced from Why Stomach Acid Is Good For You, a book that was written in 2001. Like Mercola, many of the ideas Wright put forward with the evidence to substantiate them were largely ignored by the medical profession—and much of what he proved about acid blocking medications over twenty years ago is only now starting to become accepted.
Acid Reflux
Your stomach contains acid it uses to digest food (primarily by turning on powerful enzymes which digest protein). When the stomach is digesting food, the acid should stay inside the stomach, but sometimes it instead leaks back up into the esophagus (your throat) because the muscle that seals the top of the stomach fails to fully seal. Since stomach acid is irritating, when it refluxes into the throat, it frequently creates the irritating condition known as heartburn.
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is a very common condition, estimated to affect 20% of adults (ranging between 18.1% to 27.8% of adults in the USA), is slightly more common in women, and those numbers have been gradually increasing globally. Since the heartburn it typically triggers causes immediate discomfort, people with GERD typically want it to be treated, especially once their doctor encourages this (e.g., because otherwise your esophagus can get damaged and potentially turn cancerous).
In addition to overt acid reflux, another condition also exists, known as silent reflux (or laryngopharyngeal reflux), where more minor reflux occurs without causing overt heartburn. Although I believe medicine tends to overhype diseases so more medications can be sold for them, I feel silent reflux belongs to the other camp, as it is frequently not recognized as the root cause of a variety of other symptoms such as:
•Allergies
•Asthma and reactive airway diseases
•Burning in the mouth or on the tongue
•Chronic sore throat
•Ear pressure and ear infections
•Frequently feeling like you need to clear your throat (and sometimes cough)
•Post-nasal drip
•Sensation of a painless lump in the throat
•Sinus issues
The specialty of otolaryngology (ears nose and throat [ENT] medicine) best illustrates the impact of silent reflux as a surprisingly high number of the issues patients see an ENT for are actually just due to silent reflux. In turn, better ENTs can recognize and fix those symptoms by focusing on the silent reflux rather than trying to treat the symptoms with medications directed at each individual issue. More importantly, silent reflux tends to have a greater response to lifestyle changes (e.g., eating different foods) and thus can often be easily treated without medications (although a brief course of medication is often used to help a patient recognize that silent reflux is causing their issues).
Stomach Acid Is Good For You
One of the things I always marvel at is how subtle distortions tend to occur in science which lead to everyone having a false conception of reality that conveniently allows a profitably industry to exist. One such example can be found with stomach acid, something the medical field views as largely unnecessary and thus possible to justify eliminating with acid suppressing medications.
Stomach acid for context, serves a variety of critical functions. They include:
•Making it possible to fully break down protein.
•Sterilizing the stomach so foreign bacteria, viruses, yeasts and parasites cannot make it into the digestive tract.
•Chelating minerals from food so they can be absorbed.
•Making it possible to absorb certain vitamins and nutrients (e.g., vitamin B-12).
•Regulating the rest of digestion.
Yet, most of these are glossed over. For instance, medical students are taught to believe protein digestion occurs primarily within the small intestine. This largely comes about because the critical functions of stomach acid besides digesting protein are typically barely mentioned within the medical curriculum, and for protein digestion, doctors in training are taught that the digestive enzymes from the pancreas alone are sufficient to digest protein once it reaches the small intestine, thereby eliminating any remaining need for the stomach’s acid. Within this paradigm, it thus becomes justifiable to suppress stomach acid as much as possible with acid blocking medications.
Let’s now look at why these functions are in fact vitally important.
Note: typically with medical interventions and correlated conditions, you see small to moderate correlations between them. One of the most striking things about stomach acid is over and over again how large the effect of adequate vs. inadequate stomach acid is—in most of the studies Wright cited that we will discuss in the following sections, between a two to ten fold difference could be observed once sufficient stomach acid was present.
Protein Digestion:
Proteins are composed of long chains of amino acids which then fold into a variety of complex structures which create our cellular infrastructure. To digest proteins, those chains must be broken apart and then disassembled into their constituent amino acids (which are then assembled back into proteins within the body). If this does not happen, the body becomes unable to extract the amino acids it needs from the proteins you eat, which in turn causes significant nutritional deficiencies.
Amino acid deficiency is a widespread problem, and in both my practice and that of my colleagues, we frequently find one of the most important supplements for our patients is the correct mix of predigested amino acids. Likewise, it’s frequently observed that amino acid deficiencies are linked to psychiatric conditions because some of the amino acids form the building blocks of the neurotransmitters which regulate your mood. As a result, supplementing with amino acids is often a critical component of an integrative psychiatry plan (e.g when assisting a patient with withdrawing from a SSRI antidepressant—which are notorious for being highly addictive and difficult to quit).
When proteins are not digested, their fragments are often able to pass from the gut into the bloodstream where they trigger a wide range of food sensitivities. In turn, I frequently find that with patients who have a wide range of food sensitivities (which requires them to eat very restrictive diets), their issue is poor protein digestion rather than a specific food allergy. More importantly (and a key reason why I wrote this article) was Wright’s observation that a wide range of autoimmune conditions are directly linked to low stomach acid levels.
Note: food allergy tests are fairly inaccurate and yield highly variable results (e.g., colleagues have found that two samples taken at the same time from the same patient but sent in under different patient names yielded significantly different results). I am not sure if this issue has been improved in recent years since we stopped using those tests and thus can no longer evaluate them.
Sterilizing the Stomach:
A key function of stomach acid is to sterilize the GI tract so that microbes cannot enter and colonize it (as the GI tract otherwise represents an ideal area for them to inhabit).
The importance of this sterilization is most apparent with acute infections. For example, individuals on acid suppressing medications have a much higher risk for developing food poisoning after eating a food infected with one of many bacterial species known for that (individuals on acid suppressing medications have been found to be around 4 times as likely to develop one of these infections).
Likewise, for centuries, it was well known that cholera (an infections that was a scourge to humanity until we cleaned up our water supply) was dramatically more likely to affect those with deficient stomach acid. For example, in 1885, Robert Koch (who discovered many of the fundamental characteristics of microbial infections) found that feeding guinea pigs a dose of bicarbonate (an antacid) before infecting them with cholera dramatically increased their risk of developing the infection. Likewise, in numerous cholera outbreaks, public health officials have found those who developed infections had low stomach acid levels, while those who did not had normal levels.
While cholera is now largely a thing of the past, the area where this acute infection risk is the most significant is in hospitalized patients who are routinely put on acid suppressing medications (especially if they are on ventilators). A variety of studies have shown those put on acid suppressing medications are more likely to catch those (sometimes fatal) hospital acquired infections.
For example, one study in the New England Journal of Medicine found that ventilated patients who received an acid blocking medication (which was not as powerful as the newer PPIs) were twice as likely to develop pneumonia and 60 percent more likely to die from hospital acquired pneumonia. Similarly, a Clostridium difficile infection is the leading cause of hospital-associated infectious diarrhea and has considerable impact on the length of a hospital stay and its costs—those on PPIs were found to be twice as likely to develop this condition. Furthermore, one large review of septic patients found those on PPIs were 4.3% more likely to die than those not on PPIs.
Note: the largest review that has been done so far of PPIs and COVID-19 found PPIs increased a COVID patient’s risk of dying by 77%.
Many of the issues with acid suppression are best illustrated by how they alter the normal bacterial flora of the gut. For example, to quote the manufacturer of one PPI:
As do other agents that elevate intragastric pH, omeprazole [Prilosec] administered for 14 days in healthy subjects produced a significant increase in the intragastric concentrations of viable bacteria. The pattern of the bacterial species was unchanged from that commonly found in saliva. All changes resolved within three days of stopping treatment.
While bacterial colonization in the stomach is potentially problematic, it is much more of an issue as those microbes are able to travel further into GI tract. For decades, the functional medicine community has observed that inappropriate colonization of the GI tract leads to a variety of problems, such as the complex and debilitating condition SIBO (small intestinal bowel overgrowth). Likewise, many others have linked the inflammatory endotoxins produced by bacteria within the digestive tract to a wide range of chronic health conditions.
Note: individuals with significant bacterial overgrowth in the stomach often report having a horrible breath odor (which is sometimes why they seek out treatment).
Nutrient Absorption
Many (myself included) believe one of the primary causes of all the chronic illnesses we see today are widespread deficiencies of vital nutrients. In turn, a good case can be made that this deficiency comes from any of the following:
•Intensive chemical based farming has caused our soils to become demineralized, leading to plants no longer having the nutrients we need. Given the dramatic health benefits that have been repeatedly observed from remineralizing the soil, I feel this is a very valid concern.
•Chemicals in the environment block our absorption of essential nutrients. For example, the widely used herbicide Roundup also happens to be a chelating agent which is well known for binding to essential minerals (e.g., manganese) and preventing them from entering the body.
•The highly processed food diets we eat do not have many of the essential nutrients we need (e.g., fat soluble vitamins from animal fats and organs). Weston Price’s seminal research best demonstrated the importance of this, as he repeatedly observed societies that transitioned from their traditional diet to the modern processed one went on develop the wide range of degenerative conditions associated with modern life. Likewise, I have repeatedly seen patients develop significant improvement in their health once these nutritional deficiencies are addressed.
•Nutritional absorption is impaired. While this can come from a variety of issues (e.g., dysfunctional neurological regulation of the GI tract), one of the most consequential causes is deficient stomach acid.
For many essential minerals, (e.g., zinc, magnesium, calcium, and iron), acid is necessary for their absorption as they require an acid environment to separate into water soluble ions that can enter the body (e.g., iron absorbs much better at a pH below 5). In one study, it was found antacids reduce the absorption of iron by between 28-67%, while in another study, when stomach acid deficient patients (having a gastric pH of 6.5) had their stomach acid pH lowered to 1 (making it much more acidic), calcium absorption rose five-fold to 10 percent. Similar differences are also seen with other minerals.
These issues are particularly true for minerals bound to plants when compared to the much more absorbable forms they exist as within animal tissue (which Wright illustrated with the data on iron absorption—something that may help to explain some of the fatigue and anemia seen in vegetarians).
Likewise, many essential vitamins also require stomach acid for their absorption (e.g., because acid separates vitamins from the protein they are bound to), with B12 being the best example. There is also significant data linking B6 and folate absorption to stomach acidity, and some data linking, vitamin A, B1, B2, B3 and E to stomach acid levels. Most importantly, Dr. Wright has observed improvement in the absorption of nearly every nutrient when poor stomach function is improved.
Note: a wide variety of chronic issues (e.g., excessive fatigue, reduced ability to concentrate, tiredness, insomnia and lack of interest in the external environment have been linked to B12 deficiencies). Typically Wright found in patients with chronically impaired gastric function (which was creating a variety of other illnesses), B12 often needed to be injected rather than taken orally, but in less severe cases, oral supplementation alongside supporting gastric function often was sufficient to address the problem. Additionally, he found in these patients women had the greatest response to B12.
One area Wright specialized in treating was macular degeneration. A core (but not the only) component of his approach was addressing nutritional deficiencies (which were often due to poor stomach function). To corroborate this argument, he cited a large study of the risk factors for macular degeneration:
It appears that one of the most important risk factors for a subgroup of individuals with “dry” macular degeneration (those characterized by “geographic atrophy”) is the use of antacids”
I agree with Wright’s perspective, especially since my colleague who worked with him (and held Wright in high esteem) repeated observed Wright’s success in treating macular degeneration. My only difference of opinion is that poor blood flow to the eyes (and lymphatic drainage from them) also plays a critical role in macular degeneration as I have also seen practitioners who only addressed that part of the picture (e.g., through restoring zeta potential) successfully treat macular degeneration.
Digestive Signaling
Many of the signals that facilitate digestion (e.g., the hormones secretin and cholecystokinin) are generated by the acidity of the stomach. For example, the pancreas requires those signals to release the enzymes it uses to digest proteins, once again making it very frustrating that much of the medical profession does not believe stomach acid is necessary for protein digestion. The important thing to understand is that many of these essential digestive functions can only occur within a very narrow pH range (which shifts for each stage of digestion).
Common signs of this process being impaired include indigestion or flatulence beginning an hour or more after meals and floating stools. Additionally, the pancreatic enzymatic function necessary for digestion is often observed to worsen with age and in diabetes (a disease characterized by impairment of the pancreas’s other primary function—secreting insulin).
As each of the above points show, stomach acid serves many critical functions. To quote Wright:
“Why would Nature expend so much metabolic energy to provide each one of us at birth (and until at least age forty) with an ample supply of stomach acid and pepsin if it weren’t really necessary for digestion?”
Conditions Linked to Impaired Stomach Acidity
Wright placed such a heavy emphasis on treating deficient stomach acid because he found it to be such a common thread in the patients he saw, particularly those with autoimmune conditions—which subsequently improved once stomach acid function, digestive enzyme function, and the existing nutritional deficiencies were addressed.
Many of the conditions he observed matched those which have been linked to silent reflux—which essentially means silent reflux is always an important condition to consider even if ears, nose and throat symptoms are not present. However, in addition to asthma (which can potentially be explained by refluxing stomach acid or pathologic bacteria which have colonized the stomach irritating the lungs) many other autoimmune disorders Wright treated also had a strong link to stomach acid deficiency, and for many of those disorders, he provided a strong case to support that link.
For example, in 1931, Dr. Bray published his discoveries from many years of following more than 200 children with asthma. He found that over 80% of the asthmatic children had below normal acid secretion in their stomachs, with a mild deficiency being present in 23% of the children, a severe deficiency being present in 48% and a complete deficiency existing in 9%.
In most cases, if he provided them with a dilute solution of hydrochloric acid to drink, in three months their asthma went away, with the improvement being much faster (and less likely to recur in the future—particularly over the winter) if allergens were taken out of their diet. Furthermore, he found for many children, the deficiency was the most pronounced when they were under seven years of age, and that as they grew older, many children’s stomach acid secretion returned to normal, which often coincided with the remission, or “spontaneous cure,” of their asthma.
Sadder still, Bray was not the only one to find this. Medical literature on the link goes back as far as 300 years ago and there was a wealth of data in the 1920s, 1930s and 1940s substantiating it. Unfortunately once “treatments” such as bronchodilators and steroids were found for asthma (which would be purchased for life) all incentives to explore the actual causes of asthma disappeared).
Fortunately, Wright was incentivized to use these forgotten approaches and reported:
In hundreds of cases, I have found that more than 50 percent of children who come to me with asthma can have their wheezing cured simply by normalizing their stomach acid and properly administering vitamin B12, with no bronchodilators and no corticosteroids. I can only give you approximations, but about 50 percent completely eliminate their wheezing, about 30 percent have major improvement, about 10 percent only minor improvement, and only about 10 percent no change.
Note: Wright also found acid suppressing medications provided minimal improvement for asthma.
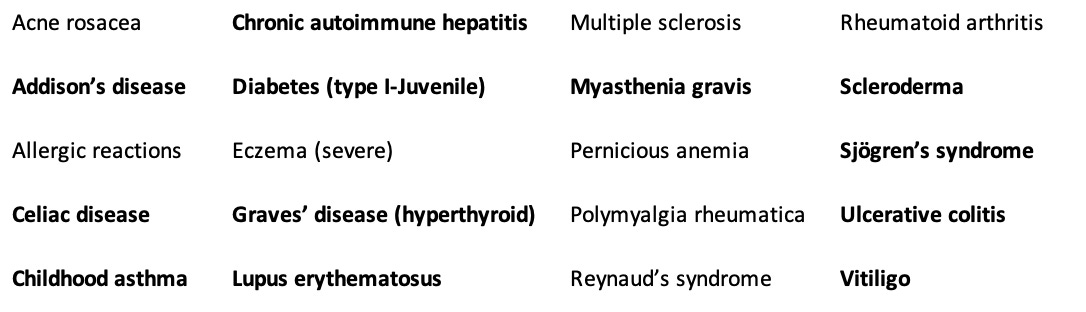
In total, Wright was able to draw a clear link between stomach acid deficiency and the following autoimmune conditions (as data existed to support the link and in over half of the cases he saw, low stomach acid was detected):
In the above list, those conditions in bold are known to be linked to an HLA genetic factor. However, despite that link, the conditions still responded to Wright’s protocol, supporting the argument that many diseases we view as being genetically inevitable are in fact only representative of an increased susceptibility to the condition which can then be treated through addressing the underlying environmental factors.
This is very similar to the situation with autism, where many different genetic factors have been partially linked to it, and all of those factors share the common thread of increasing the likelihood an environmental toxin will permanently damage the body (e.g., because its ability to detoxify is reduced, because the body has an increased sensitivity to entering the cell danger response, or because the body has a decreased ability to maintain its physiologic zeta potential). Thus in both cases, we have a myriad of conditions that are difficult to explain unless they are each viewed as the manifestation of a few key pathologic processes.
In addition to these autoimmune disorders (which Wright typically treated by restoring gastric acidity, replacing the lost nutrients and avoiding foods the patient had a sensitivity too), he observed a variety of other conditions were also frequently triggered by low acidity. These included:
•A variety of GI related issues (e.g., bloating, poor digestion, poor absorption of nutrients, SIBO, and of course GERD).
•Skin diseases, including forms of acne, dermatitis (itching, redness, swelling), dermatitis herpetiformis, eczema, and urticaria (hives)—many of which are technically autoimmune disorders.
•Accelerated aging
•Depression
•Gallbladder disease (gallstones)
•Hay fever (which is also allergic in nature).
•Macular degeneration
•Migraine headaches
•Osteoporosis
•Stomach cancer
Note: In his 2001 book, Wright predicted the PPIs would significantly increase stomach cancer, since as early as 1879 the condition had been linked to low stomach acid conditions (possibly as a result of allowing an H.Pylori infection to become more damaging). Recent studies have confirmed this prediction, typically finding PPIs roughly double the rate of stomach cancer (e.g., a meta-analysis reviewing millions of people found PPIs increased it by 1.8 times).
What Causes Acid Reflux?
So far, I’ve tried to make the case that acid reflux is tied to a stomach acid deficiency (something Wright found in over 90% of the thousands of tests his clinic performed), and more importantly, that the presence of reflux should serve as a warning that other parts of your health may also be compromised due to it suggesting the presence of a stomach acid deficiency. Sadly, doctors always assume there is too much acid in the stomach when seeing a patient with GERD rather than measuring the stomach acid levels prior to beginning an acid reducing regimen (e.g., in 30 years of practice, Wright never saw a patient who ever had their stomach acid directly measured by another doctor, regardless of how many tests their previous doctors had performed to evaluate their GI tract).
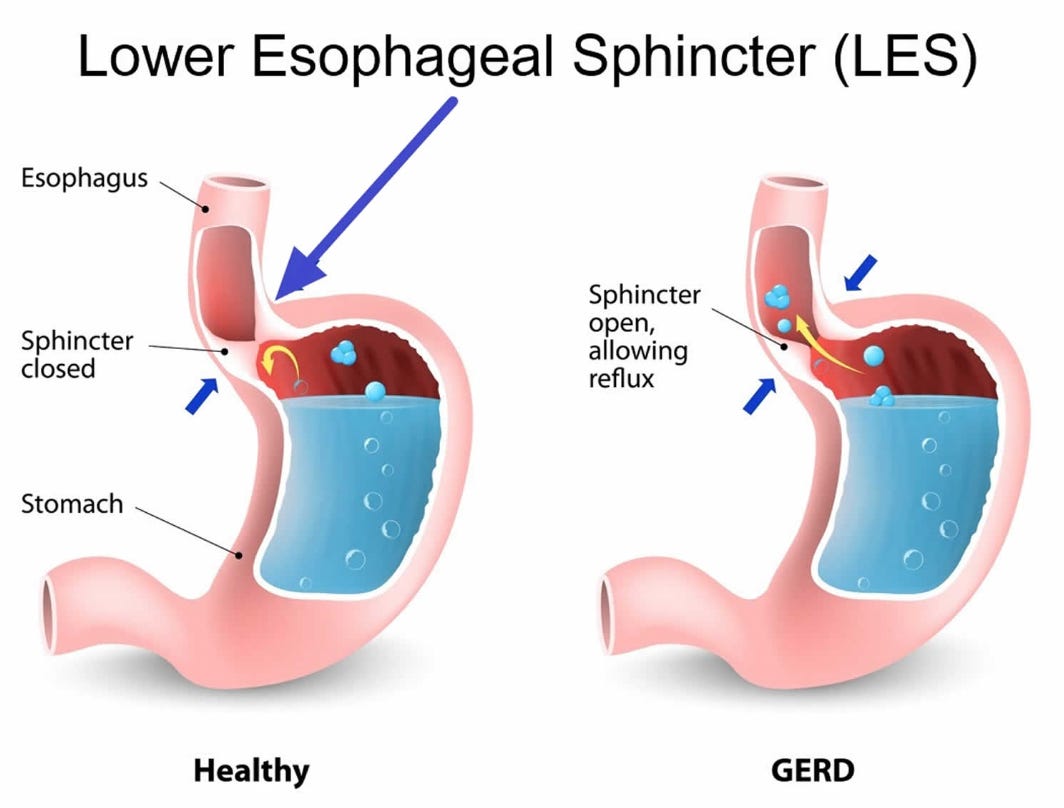
All of this comes about because of an important fact that is never taught in medical school. The lower esophageal sphincter is pH sensitive and only closes once sufficient acidity is present in the stomach (which makes sense since otherwise food would not be able to get to the stomach in the first place, but once it’s there, you need a way to keep it from getting back into the throat).
Since GERD is so common, that suggest there is also a widespread deficiency in stomach (hydrochloric) acid. Presently, I believe a few factors are responsible:
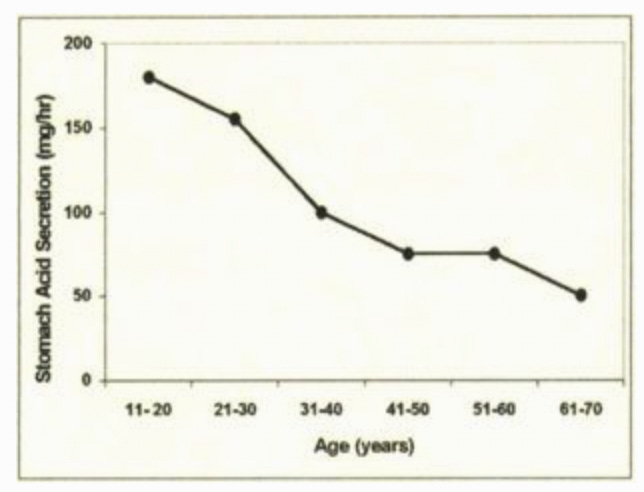
•The first is that stomach acid production is known to decrease as we age (particularly after 60), and at this time, I consider it to be one of the primary causes of the degeneration seen in aging and why, amongst other things, amino acid and B-12 supplementation is often so critical for older patients.
Note: The likelihood of GERD is known to increase with age, which again makes it remarkable so few doctors consider the possibility excess acid in the stomach is not the cause of their patient’s symptoms or think to ask (to quote Dr. Wright):
Why is too much acid so efficient at refluxing back into the esophagus but so inefficient at actually digesting food?
•Second, stomach acid requires both hydrogen and chloride to be produced, and many of the dietary factors which created each (e.g., unprocessed sodium chloride) are much less present in our diet now. In turn, colleagues have found correctly supplementing these elements often significantly improves GI function.
•Third, autoimmune conditions can attack the acid producing cells of the stomach.
•Fourth, H. Pylori infections will decrease stomach acid production.
•Fifth, stomach acid production is an energy intensive process (hence the cells which make stomach acid having a large number of mitochondria), and I have long suspected that mitochondrial dysfunction (something often also seen with many of the chronic illnesses Wright listed above) is partly responsible for declining stomach acid levels.
•Finally, taking acid suppressing medications, does of course reduce the presence of stomach acid.
However, at the same time, a stomach acid deficiency is not the only thing which can cause reflux. It can also frequently occur if too much pressure is on the stomach (e.g., from a hiatal hernia—a condition estimated to affect 55%-60% of individuals over the age of 50), thereby popping the lower esophageal sphincter (LES) open. Likewise, many medications, particularly ones used to relax muscles like the bronchodilators used to “treat” asthma, certain blood pressure medications (e.g, calcium channel blockers) along with valium, nitroglycerine, and opioids, all relax the LES and thereby allow stomach contents to leak through it. Additional, Wright found that some foods, including fats, chocolate, coffee, other caffeinated beverages, mints (especially peppermint and spearmint), sugar, onions, and some alcoholic beverages, can weaken the LES.
Finally, if a substance irritates the stomach, that will frequently trigger reflux to occur. Some of the most common triggers include acidic citrus fruits and tomato-based foods, spicy foods, carbonated beverages, and coffee. Additionally, for patients with lectin sensitivities, the high lectin foods are often important to avoid.
It should also be noted that a food irritating the stomach is not always bad. For example, spicy or bitter foods trigger stomach acid secretion, and in many parts of India, incredibly spicy foods are the standard cuisine—something many of my colleagues have suspected emerged in the culture because it protects the natives from the high number of parasites there (as the stomach acid kills them). However, while spicy foods (specifically the active ingredient capsicum) trigger acid secretion and have a protective effect on the stomach’s lining, they will also irritate already inflamed tissue and hence should not be used in more severe cases of GERD.
Note: the foods listed above are typically seen on lists of foods to avoid if you have GERD, but Wright is the only person I know of who broke them into foods that weakened the LES versus foods that irritated the stomach.
The Problems with PPIs
Presently, it is estimated that over 27% of Americans take antacids, and that over 15% of the USA population (increasing with age) take PPIs. For context, PPIs are the most powerful acid suppressing medications—a single pill often removes almost all of the stomach’s acid for the rest of the day—but simultaneously are sold over the counter allowing many to self-medicate with them.
Note: some antacids (PPIs and H2 antagonists) work by suppressing the stomach’s acid production. Others (e.g., Tums) work by directly neutralizing acid within the stomach. Although the neutralizing ones are the least harmful (since they have the weakest effect on stomach acid production), many of those neutralizers contain aluminum hydroxide (a toxic compound which severely impairs physiologic zeta potential and is frequently added to vaccines as an adjuvant). Because of this, it is important to review the ingredients of antacids before you ingest them.
From reading this article so far, you can likely guess what many of the harms from PPIs are, and when they were first approved by the FDA, many of those harms were recognized. As a result, PPIs were intended to only be used for rare conditions (e.g., Zollinger–Ellison syndrome) characterized by very high stomach acid levels or in the presence of significant damage to GI tissue, and if used, to only be used for a 4-8 week period.
Since there was so much money to be made in using PPIs, we instead saw patients use them for much more common issues (e.g., heartburn) and often for the rest of their lives. Furthermore, since GERD is often due to too little stomach acid preventing the LES from closing, once a PPI is stopped and a bit of the stomach acid returns, rebound GERD often immediately occurs before a normal stomach acid level is reached and the LES closes on its own. As a result, after a prolonged period of use, PPIs are often extremely difficult to quit (e.g., consider that there have been reports of patients who produced no stomach acid for two years after stopping Prilosec, a common PPI that you can now buy over the counter).
Note: a medication which demonstrated short term benefit becoming problematic when it instead was used for a prolonged period is a recurring issue in medicine—since overuse is always what benefits the pharmaceutical industry. One of the best examples are the benzodiazepines (like valium) used for anxiety. These drugs can be very helpful when used for brief periods of intense stress, but become extremely detrimental and addictive once they are used indefinitely, leading to many patients becoming chronic users of the drugs. Two of the other drug classes that are the most notorious for creating a lifelong addiction due to their severe withdrawals are SSRI antidepressants and opioids.
Likewise, now that the PPIs are off patent, research has at last begun to emerge that has corroborated many of Wright’s predictions about PPIs from over twenty years ago. For example in addition to the harms listed previously (e.g., impaired nutrient absorption or an 80% increase in stomach cancer), PPI use has now been linked to:
•A higher risk of dying (e.g., this study found PPIs increased the overall risk of death by 19%).
•A higher risk of a major cardiac event (e.g., this meta-analysis found a 28% increase)
•Kidney disease (e.g., this study found a 74% increase in severe kidney disease, resulting in a 142% increased risk of death for those patients).
•Liver disease and a significant worsening of existing liver disease.
•Osteoporosis and fractures
•Infections such as the previously mentioned Clostridium difficile colitis. For example, this study found a 37% increased risk of community acquired pneumonia in PPI users.
•Hypomagnesemia (low magnesium levels).
•Dementia (e.g., this recent study found a 33% increase).
Managing Stomach Acidity
Most of the existing approaches for treating GERD (excluding those which use acid suppressing medications) and the conditions relating to deficient stomach acidity normally seek to do one or more of the following:
•Reduce the pressure on the stomach.
•Remove irritating foods from the diet.
•Restore the tone of the LES.
•Restore hydrochloric acid production.
•Heal damaged areas of the GI tract (e.g., an ulcer) without using acid suppressing medications.
•Support normal digestive function in tandem with increasing stomach acidity.
Some of these approaches are relatively straightforward and have been mentioned throughout the article. Others are commonly done within medicine (e.g., a fundoplicationwraps the top part of the stomach around the esophagus thereby tightening the LES and reducing how much acid can exit back into the esophagus—but unfortunately has a variety of side effects).
Many of the effective approaches I and colleagues have used to address GERD and the complications of low stomach acid are muchsafer than a fundoplication. Unfortunately, there are still precautions with using them, and I ask you to consider everything in the final part of the article (and ideally find a physician to work with) before attempting any of it.


No comments:
Post a Comment