Corona virus a sensor disease spreading worldwide through misusing of processed radio frequency and all the PATENTS
In my substack i have over 100 CORONAVIRUS, SARS, MERS AND THE SENSORS PATENTS you'll just have to go dig through it you'll find them( LINKS BELOW)
Todd Callender – BOMBSHELL Discovery Documents Confirm Targeting Populations Through Wireless Tech https://zeeemedia.com/interview/todd-callender-bombshell-discovery-documents-confirm-targeting-populations-through-wireless-tech/ if you haven't been over to my older substack articles total exposure yet to find the coronavirus PATENTS maybe you will after this article Hh https://open.substack.com/pub/operationsavehumanity/p/can-you-say-viruses?r=24qa7g&utm_campaign=post&utm_medium=web https://open.substack.com/pub/operationsavehumanity/p/severe-acute-respiratory-syndrome?r=24qa7g&utm_campaign=post&utm_medium=web https://open.substack.com/pub/operationsavehumanity/p/a-new-class-of-protein-sensor-links?r=24qa7g&utm_campaign=post&utm_medium=web there's more! Go look! Corona is a non-communicable sensor disease spreading worldwide through misusing of processed radio frequency. So far higher authorities of health services are facing the undesirable escalating causes of coronavirus towards human beings as a very scientific puzzle comprehensive issue. The study aims to evaluate the maltreating of wireless sensor networks that affect individuals within the body boundary area. Wireless sensor data were collected from individual’s profile, diagnosis and sensor node records at laboratory experiments. The study shows the effect of processed sensor nodes among individual’s body organs to compare with the existing environments. The study illustrates all individuals suffer from sensor disease due to reflecting of wavered sensors at open eyes sights with high speed electromagnetic-radio tracking systems.
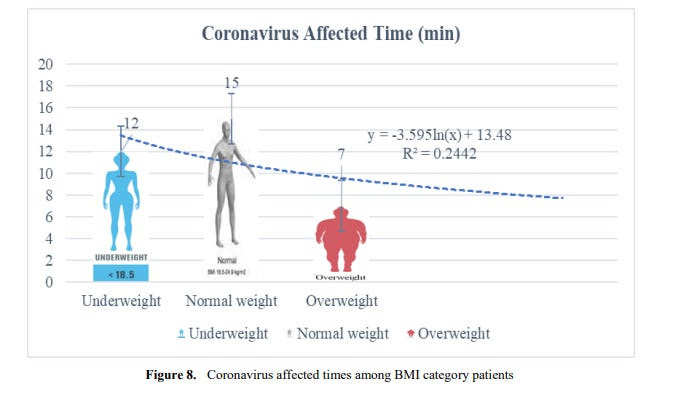
The overweight and obesity patients are sick from corona disease at less sensor time in a dark environment than that of light conditions. These findings replicate the severe global one health security that the expert provides in active eyes within geographic locations. Systematic healthcare awareness is essential for treatment with medical technological devices but such consciousness is poorly recognized and medication supports are still below par
. The study suggests upcoming healthcare paths of a new dynamic alternative approach to promote global public health security concerning Sensor Health Policy and Sustainable Development Goals 2030
.
Now a day’s medical sensor technology is essential in every step of healthcare. Wireless Sensor Network is an integrated infrastructure comprising sensing, computing, detecting, tracking, observing and reacting the individuals within geographic positioning systems (GPS) locations [14]. This network deploys the indoor and outdoors in large sensor fields using the object's light and radio signal
.
Wireless sensor networks are premeditated to achieve the scarcities like dimension, tracking, detection and cataloging, s, simulation particularly the field of health monitoring [14]. A harmonized amount of medical technologies has been organized for patients’ monitoring who suffer from severe diseases or have urgent prerequisites [27]. Wearable health-monitoring provides a revolutionary sensor technology, which serves as an alternative to traditional diagnosis, putting healthcare data on a path that is more remote, portable, and timely. Physicians and health researchers use these healthcare data to evaluate body conditions with a sensor technology like internet of everything, artificial intelligence, deep-learning algorithm. Moreover, sensor technology has a great advantage on non-communicable diseases to identify the classical symptoms [14]. Wireless sensor networks are a huge endeavor of digital health technology, including technology dependence, which has led to frustration due to lack of proper security. Smartphones can do a lot of lucrative things with at least 12 functions with digital health sensor systems. Cyber hackers misuse the radio frequency through smartphones, telematics and high frequency sensor devices for spreading this corona remote sensing VIRUS (Vital Information Resource Under Siege) among animals and human beings, mostly coronavirus.
The rationalized generations involve in good or harm activities to any human in the world through wireless sensor networks through hidden codes [14]. The present world is being one-sidedly mistreated sensor networks one after another from cyber hackers.
Corona virus …Its man-made sensor programming virus, which can make people and animals sick by tracking them at specific GPS distances by adjusting the retina of human and animal eyes through sensor devices. This was revealed in 2018 through the ISNAH test in PhD research at UNIMAS (Universiti Malaysia Sarawak) in Malaysia. The PhD thesis was approved by the Senate of UNIMAS on May 20, 2018. Since then, the study has been trying to inform the people of the world about the findings of the PhD research from 2018 to date, but cyber hackers are creating obstacles in various ways. This is because, “some people (through the misuse of technology) are wreaking havoc on water and land all over the world” [87]. In 2018, the name of the study on sensor technology test was "ISNA-Impact of Sensor Networks towards Animals", and in 2019 it was called "Corona" at Wuhan, then WHO declared as COVID-19. The symptoms that appeared during research on dogs and cats are exactly the same in people infected with the coronavirus.
So, corona is not spread by bats, humans or any other animals, it was not made in any scientific lab like the Wuhan Institute of Virology [101], but cyber hackers spread corona disease in humans and animals’ body through cloud sensing devices due to misusing of wireless sensor networks at certain GPS distances [15]. Mask, handwash, social and physical distance and vaccines are not completely recovery pathways, but cyber hackers send messages with false interfacing to the higher authority.
The study necessitates an integration of methods used in wireless sensor networks towards animals’ bodies and identified its implication. This envisaged the research taking in matter-of-fact research elements to investigate issues hoisted in the study, primarily targeted at SMART devices like telematics’ users towards specimens. Telematics is a smart device, consisting of a scanner, recognizer, detector, global positioning systems (GPS) and global navigation satellite systems (GNSS). The fieldwork conducted in the studied area within January 2015 to January, 2017. ISNAH Experiment is the novel and uniqueness experiment which includes the Impact of Sensor Networks towards Animals [40]. The ISNAH process showed the necessary components in Figure 2. This is a multi-diversified experiment in connection with sensor technology to augment non-communicable diseases among animals and the human body.
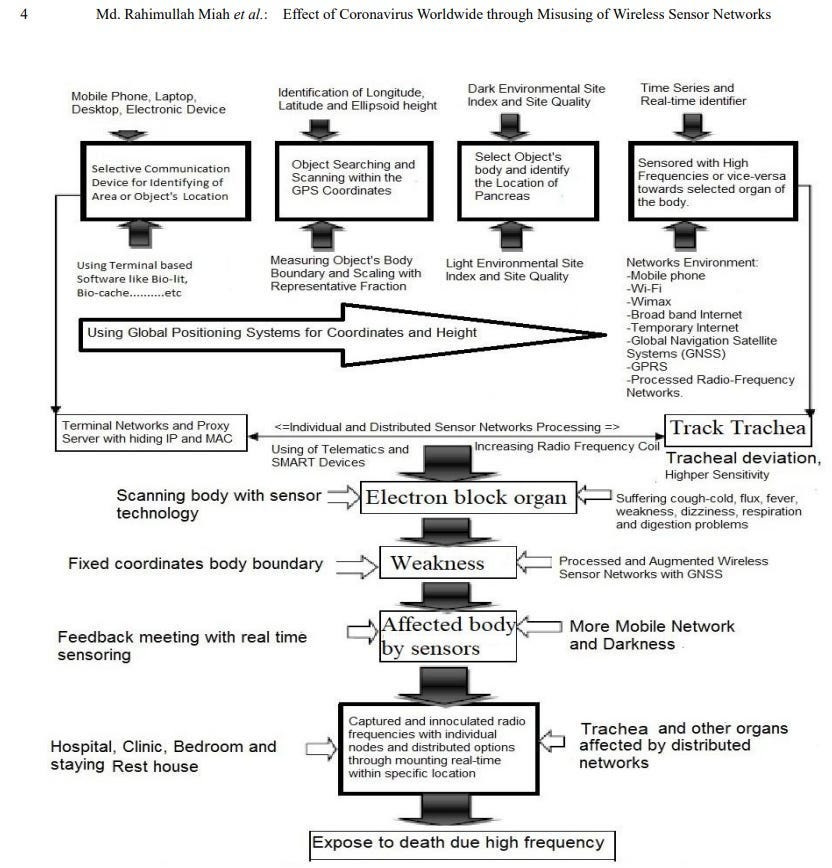
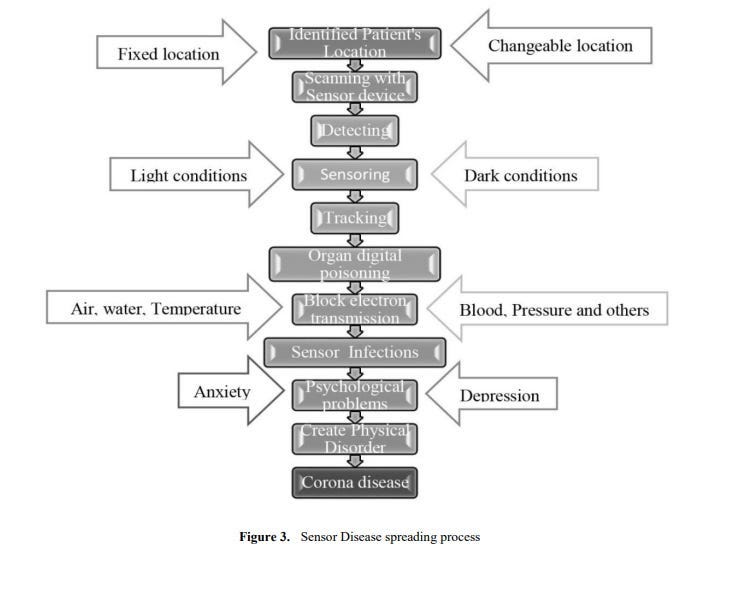
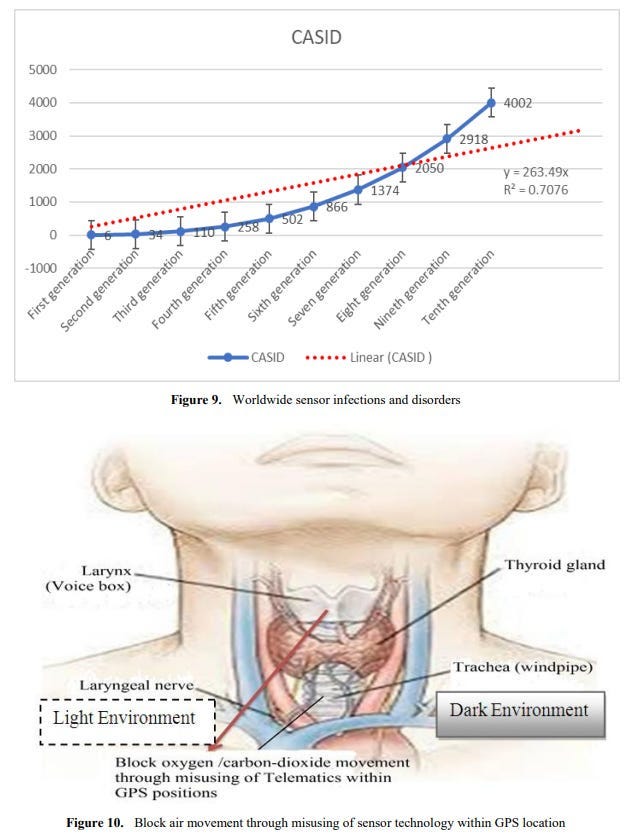
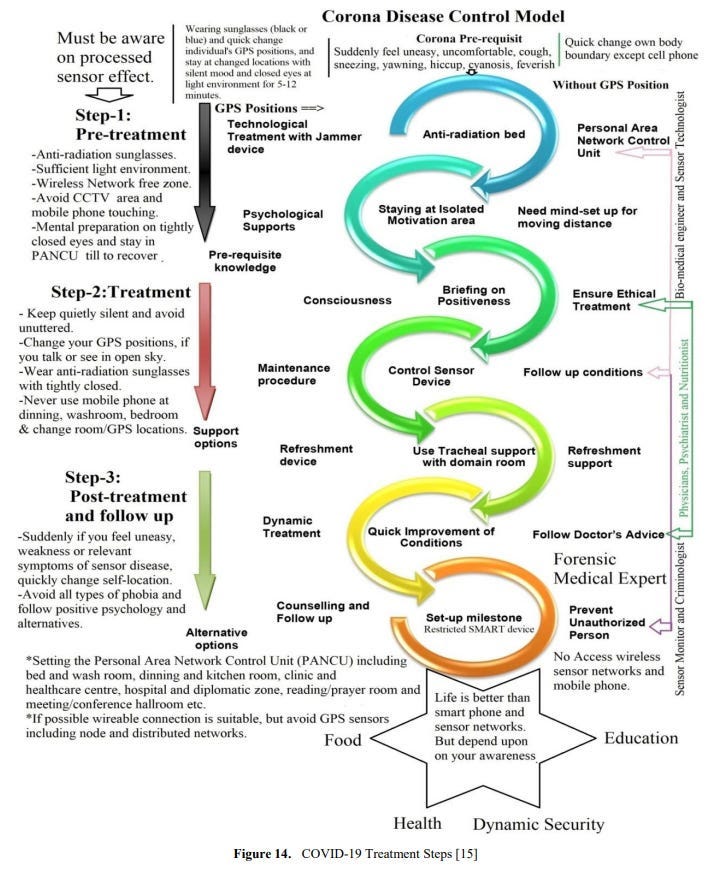
Sensor Disease Spreading Process Common Acute Sensor Infections and Disorders (CASID) is the new term, which indicates the sensor diseases produce and spread through processed radio frequency of advances in sensor technology. When this processed radio frequency is tracked in GPS positions towards living cells, particularly human beings and animals’ bodies. The sensed living cells block electron movement and produce different types of disorders or diseases in the affected organ of the body. The CASID implies a formula as, C = 4N3 + 2 (i) Where, N= the number of sensor network generation processed response signals. C= the producing sensor diseases including CASID. The cyber hackers are misusing the wireless sensor technology due to expanding processed radio frequency coil at longitude, latitude and ellipsoid heights. These processed radio frequencies are disseminating to a human body’s GPS coordinates points through a clouding system around the world. The cyber hackers are staying at geographic locations and produce different types of diseases, particularly Coronavirus disease in the human body. The hackers select the specific organ of the body as a fixed GPS location, including (i) Office room, (ii) dining room, (iii) Bed room, (iv) Wash room, (v) Meeting and conference room, (vi) Media / communication room, (vii) Computer / Network Server room, (viii) Mobile / Telephone room, (ix) TV / Theatre room, (x) kitchen, (xi) Dressing room, (xii) Healthcare room, and (xiii) Other GPS location. The sensor disease can produce through the following steps, which as shown in Figure 3.
From the ISNAH experiment, the study represents human body transmission with sensor disease, particularly coronavirus disease or COVID-19 in a light environment.
Occurrence of Coronavirus Infection with Sensors For coronavirus infection, Cyber hackers first scan the sensor via GPS to confirm the current location of the person, animal or object and create symptoms of the corona. Cyber hackers can then censor certain parts of your body to make you sick, depending on the distance of the frequency, or to stop your breathing through the misuse of sensor technology. And if you stop breathing, your death is certain. Thus, by misusing node frequency, a person or an animal can be made sick or killed in corona and by misusing distributed frequency, people, animals, cows, goats, poultry, birds, fish or other animals can be made sick in corona together.
Coronavirus Disease Spread through Wireless Sensor Technology Telematics is a type of sensor light made with sensor technology, which works in combination with atmospheric waves. Cyber hackers are scanning the retina of the human eye to know the current location and monitor every moment. As a result, your location will be known immediately wherever individuals open their eyes at the country or international border and their activities will go to the sensor server with the picture. Because the sensor network is adjusted to your vision in the atmosphere. In addition, individuals are sitting / lying in the office or at home, working, eating, sleeping, etc. on a daily basis. At this time, even if you have a mobile phone or sensor device around you, your location is easily known. Moreover, even if you do not have a mobile phone, your location can be known through words, laughter, tears, high-cough or open eyes. Cyber hackers find out the distance of different parts of your body from your surroundings through telematics devices, then digital scanning is done from the neck to the head of your body with software like CT (Computed Tomography) scan or MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imagery). Then the low frequency electromagnetic sensor force is applied to the voice box and trachea of the place through smart remote sensing with the help of telematics. For a while, the person feels a tingling sensation, body temperature rises, sneezing-coughing, or high-hiccups and body fades, runny nose, loss of appetite, and dryness in the airways.
If a person suddenly suffers sneezing, hiccups, coughing, cyanosis, runny nose, flatus, chills, headache, discomfort or gasps after being in a certain place, immediately closes his eyes, wears sunglasses (anti-radiation glass), clothes black cloths and quickly changes his existing place to a new place. This is must do. ii. The person can then wear sunglasses (anti-radiation glasses) with their eyes closed for at least 7 to 25 minutes in the new place, if the body feels abnormal or weak. No mobile phone, electronic device, telematics, GPS (Global Positioning System) or any sensor device will be with you while you are in the new place, but personal area network control unit (PANCU), anti-radiation bed, radiation free mosquito net can be used.International Journal of Biological Engineering 2022, 7(1): 1-13
DOI: 10.5923/j.ijbe.20220701.01
Impact of Processed Wireless Sensor Networks on
Biodiversity Conservation
Md Rahimullah Miah1,2,*, Md Mehedi Hasan3, Jorin Tasnim Parisha4, Md Sher-E-Alam5,
Alexander Kiew Sayok2, Md Shoaibur Rahman6, Md. Amir Sharif7,
Mohammad Belal Uddin8, Shahriar Hussain Chowdhury9
1Department of IT in Health, North East Medical College and Hospital, Affiliated with Sylhet Medical University, Sylhet,
Bangladesh. and PhD Awardee from the IBEC, UNIMAS, Sarawak, Malaysia
2Research Fellow, IBEC, Universiti Malaysia Sarawak (UNIMAS), Kota Samarahan, Sarawak, Malaysia
3Department of Law, Green University of Bangladesh, Dhaka, Bangladesh
4Government Satis Chandra Girls’ High School, Sunamganj Sadar, Sunamganj, Bangladesh
5Department of Law and Justice, Metropolitan University, Sylhet, Bangladesh
6Department of Agroforestry and Environment, Hajee Mohammad Danesh Science & Technology University, Dinajpur, Bangladesh
7Department of Accounting and Information Systems, Begum Rokeya University, Rangpur, Bangladesh
8Department of Forestry and Environmental Science, Shahjalal University of Science and Technology, Bangladesh
9Department of Dermatology, North East Medical College and Hospital, Affiliated with Sylhet Medical University, Sylhet, Bangladesh
Abstract An explorative field observation to determine the impact of wireless sensor networks on biodiversity
conservation at national parks in Bangladesh that was conducted in plants, animals and landscape. Everyone is using
advanced wireless sensor networks, but no one is fully aware of its impact on conserving biodiversity. Plausible wireless
sensor device has given people mobility, while also embracing wildlife’s mental disorders associated with risks in their living
places. That is why some strive for success, while others are frustrated by abuse of wireless sensor technology towards
biodiversity. Biodiversity is an important instrument to sustain life. Everyone uses its benefit globally but none can conserve
it in an effective manner at national parks. Yet environmental conservation experts have been facing the unexpected losses of
biodiversity in every sphere as a very important global issue for several years. Biodiversity experts are looking for the right
way to restore biodiversity for present and upcoming generations. The study aims to identify the root causes of losing
biodiversity at Lawachara National Park in Moulvibazar district to stare as a study in regional issues. Quantitative and
qualitative related park conservation data were collected from laboratory experiment, field observation, while secondary data
were obtained from miscellaneous sources. The study highlights the impact of sensor networks with ISNA (Impact of Sensor
Networks towards Animals) experiment on wildlife to be compared to feline body mass indices in a light and dark
environment. The study illustrated the excess weight wildlife is about to die within 5-12 minutes due to processed tracking
and digital poisoning in light environments due to active open eyes and staying at a fixed GPS location. The study also shows
frequent sickness within 12-25 minutes for the underweight wildlife in the same environment, facilitating design and use of
modular tags. The research replicates the risk of visitor’s access to national parks with smartphone and high frequency sensor
devices. These findings reflect the importance of conserving biodiversity at national parks that the State provides. A dynamic
national park area wireless network control unit and adaptable solution has been anticipated with a restricted peripheral
network system for biodiversity protection.
Keywords Biodiversity, National Park, Wireless Sensor, Policy, Secure Technology
1. Introduction
Biodiversity conservation generally develops strategies
connecting the supportive assortment of environmental
policy instruments. These conservation instruments interlink
* Corresponding author:
drmrmiah@yahoo.com (Md Rahimullah Miah)
Received: Nov. 18, 2022; Accepted: Dec. 12, 2022; Published: Dec. 23, 2022
Published online at http://journal.sapub.org/ijbe
with six principal goals of the strategy including (i) National
Park Biodiversity Conservation, (ii) Sustainable use of
ecosystem services, (iii) Reducing environmental pollution,
(iv) Access benefits sharing of genetic resources, (v) Digital
conservation with Biodiversity Clearing House Mechanism,
and (vi) Raising social awareness for biodiversity
conservation as one of the top priorities to society.
Different instruments are sometimes combined into a
2 Md Rahimullah Miah et al.: Impact of Processed Wireless Sensor Networks on Biodiversity Conservation
policy mix to address a specific environmental problem
for biodiversity conservation. These biodiversity loss causes
and environmental problems are usually caused by
over-exploitation of natural resources, misuse of technology,
services and systematic product consumption patterns [1].
Rapid loss of biodiversity remains one of the foremost
conservation issues as it potentially disturbs ecosystem
functions [2,3,4,5]. Damage is one of the most
thought-provoking global environmental concerns [6],
which has emerged as a dominating problem worldwide
for several years on the coasts of various planets [7].
Everyone exploits biodiversity but none can conserve
it in the absence of dynamic policies, institutional support,
stakeholder engagement and ecotourism services, invasive
alien species control measures and application of
conservation technologies [8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17].
Thus, appropriate and specific policies are needed to prevent
rapid loss of biodiversity. National Parks (NPs) are often
targeted at lands where there is the least political resistance
to their establishment and thus generally face anthropogenic
threats. Due to the lack of accurate assessment, the
development of indicators and indicators can lead to
an understanding of updated rules and regulations related
to biodiversity, which allow changes and trends to be
monitored and adapted over time [18]. To date, no up-to-date
comprehensive model incorporating various relevant
political, environmental, socio-cultural, technical, economic,
institutional and legal processes [18] for national park
biodiversity management has been developed.
The study highlights how to stimulate sustainable use of
ecosystems to incorporate many of these elements, including
stakeholder engagement, institutional participation, updated
policy integration, and conservation technologies. This study
explains biodiversity conservation for LNP management
with the tools needed to study changes in conservation
systems and their implications to provide rational policy
and advanced wireless sensor technology options. To date,
no comprehensive model has been developed for national
park management to conserve biodiversity in developing
countries that incorporates various relevant environmental,
economic, technological, institutional, personal and social
processes. Research aims to improve biodiversity policy
options and technology applications.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Tools
The study site is situated in the civil administrative units of
Kamalganj sub-district, Moulvibazar district under Forest
Administration Unit, Bangladesh [19]. The study followed
the materials and methods from the URLs [a-i]:
a. URL: http://article.sapub.org/10.5923.j.geo.20211101.02.html (Loss of wetland biodiversity and Technology)
b. URL: http://article.sapub.org/10.5923.j.env.20211102.01.html (Climate Crisis and Technology)
c. URL: http://article.sapub.org/10.5923.j.ijvmb.20211001.03.html (Numbness and Technology).
d. URL: https://ir.unimas.my/id/eprint/24535/ (Biodiversity conservation and Policy Instrument)
e. URL: http://article.sapub.org/10.5923.j.re.20221203.01.html (Man-made Technological Heatwave)
f. URL: https://ccsenet.org/journal/index.php/gjhs/article/view/0/46717 (Environmental disease and Technology)
g. URL: https://www.ccsenet.org/journal/index.php/jsd/article/view/0/40313(Psychological conservation)
h. URL: https://www.un-pub.eu/ojs/index.php/wjer/article/view/5855 (Policy on Environmental disease)
i. URL: https://ccsenet.org/journal/index.php/jpl/article/view/0/47787 (Society and Environmental disease)
The study showed the site map at Lawachara National Park’s biodiversity, which as shown in Figure 1.
International Journal of Biological Engineering 2022, 7(1): 1-13 3
Figure 1. Lawachara National Park at Kamalaganj in Moulvibazar, Bangladesh [20,21]
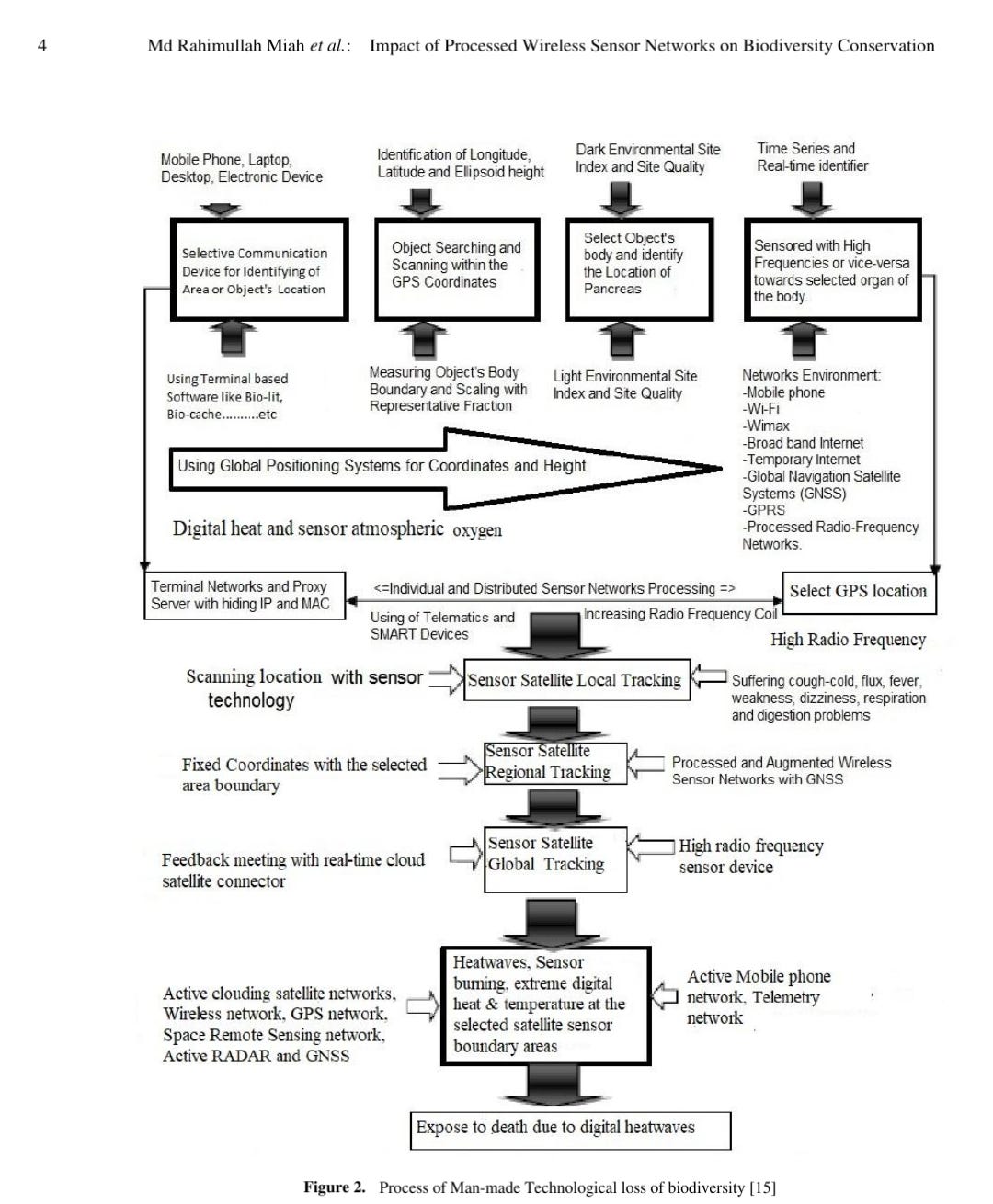
Sensor Tracking towards the tree, dog and cat species at
different specific GPS location including longitude, latitude
and ellipsoid height in different steps, which as shown in
Figure 2.
2.2. Procedure on Technological Loss of Biodiversity
All quantitative and qualitative related biodiversity data
are collected and compiled according to the research
objectives. These compiled data are also checked for
accuracy from various sources to prepare master sheets for
analysis and interpretation using updated software like MS
Office 2021, R ver. 3.6 and SPSS ver.29.
4 Md Rahimullah Miah et al.: Impact of Processed Wireless Sensor Networks on Biodiversity Conservation
Figure 2. Process of Man-made Technological loss of biodiversity [15]
3. Results
From the study of misuse of wireless sensor device, it
observed that the examined species- cat and dog were felt
sleepy and after few moments, they could not breath properly,
as a whole, they were about to die. Immediately cell phone
removed and disconnected from the study area. During
medication time, the study also observed that both animals
felt pain at their throats separately. The study identified that
the animals were suffered from cough-cold and fluctuated
body temperature. The telematics device also affects on
tracking effective time to animals, which as shown in Table
1.
Table 1. Tracking effective time to animals
Type of
animals
Environment
Impact
Light
Dark
Less
weighted
More time
(25 minutes)
Less time
(15 minutes)
Sleepy and
weakness
Heavy
weighted
Average
(12 minutes)
Less time
(7 minutes)
About to die
International Journal of Biological Engineering 2022, 7(1): 1-13 5
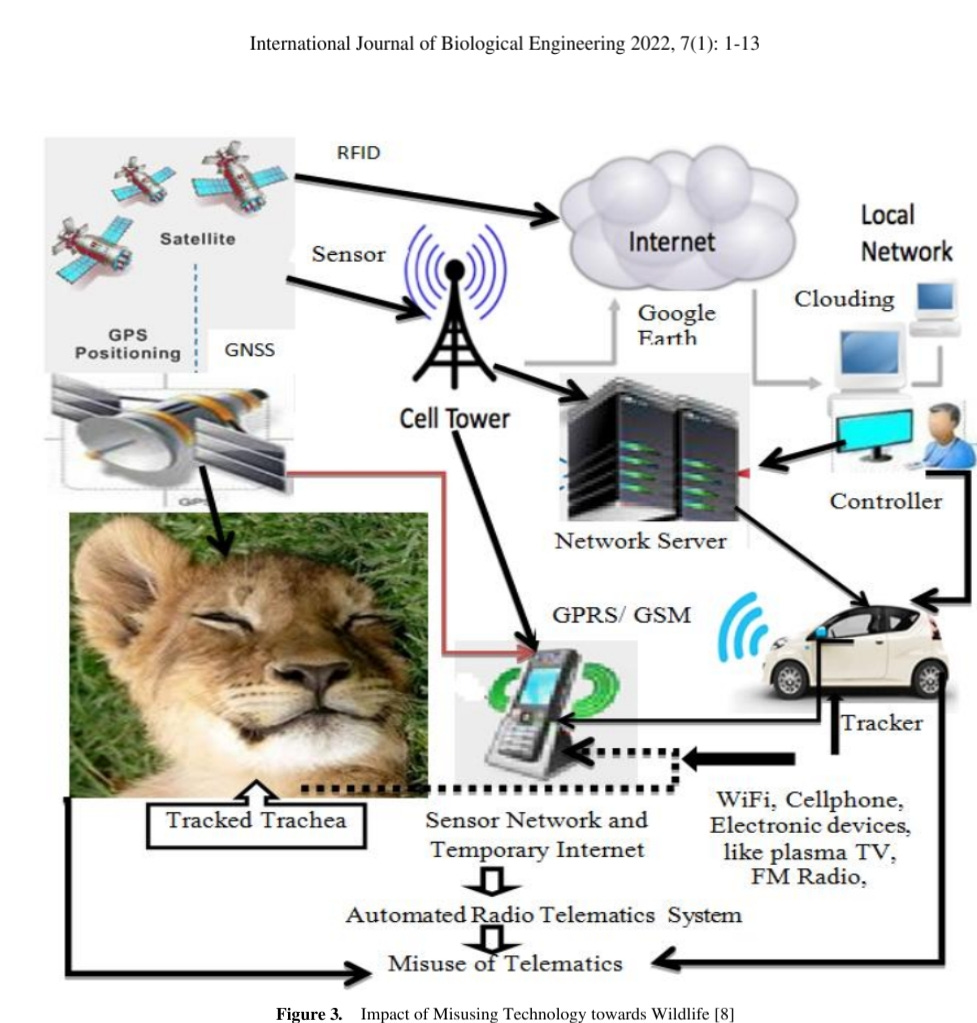
Figure 3. Impact of Misusing Technology towards Wildlife [8]
These animals were affected pain at tracheas by sensor
networks, which were transmitted from the telematics
technology as shown in Figure 3. During the experiment,
it was also identified that the tracker tracked the animal
through scanning temporal landscape including longitude,
latitude and elevation using global navigation satellite
system, which was connected with GPS and GPRS, cell
phone and Wi-Fi networks. It is mentioned that the
Automated Radio Telematics System includes wireless
sensor network, active open eyes and switch-on smartphone.
However, the study illustrated that loss of biodiversity at
Lawachara National Park (LNP) occurs through the
misapplication of modern technology, particularly macaque
monkey declining.
Due to misuse of advanced wireless sensor technology,
the impacts of illegal logging are varied, ranging from
unchecked deforestation to the deprivation of sustainable
livelihood opportunities for local communities of Lawachara
National Park areas. Besides, there are some areas; those are
risk for illegal logging and poaching, as shown in Figure 4.
The study also revealed the wildlife suffer from sensor
diseases like tracheal cancer, coronavirus disease, acute
respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), cardiac arrest,
Numbness, Neurofibromatosis, Stomach cancer, Liver
cirrhosis, falling down, fever, dermal disease etc. due to
tracking with advanced wireless sensor device at a specific
GPS location and active open eyes.
Here the symbols expressed as: A= Adjacent Bharaura,
B= Adjacent Fulbari Tea Garden, C= Adjacent Magurchera,
D= Adjacent Gilachara Tea Garden, E= Adjacent Langurpur,
F= Adjacent Bagmara, and G= Adjacent Garobosti areas.
Out of these areas, adjacent area of Bharaura is the most
highly risk area for poaching and illegal logging— according
to the opinions of Focus Group Discussion and Informal
survey. Moreover, Illegal logging tends to deforestation,
which creates loss of LNP’s biodiversity. According to
World Bank (2012) estimates, illegal logging is the results in
a loss of approximately USD 5 billion in tax revenue for
government annually. Bangladesh Forest Department (BFD)
maintained its efforts to tackle illegal logging since the
establishment of co-management system at LNP.
6 Md Rahimullah Miah et al.: Impact of Processed Wireless Sensor Networks on Biodiversity Conservation
Figure 4. Risk areas in Lawachara National Park for poaching and illegal logging (Source: Google Map, 2018)
Figure 5. The percentage of Forest Area Changes from 1990 to 2015 in Bangladesh
Conservation policy instruments exist at all stages of the
policy process with specific tools— in-situ instrument, for
example national park. From the result, it is shown that the
Lawachara National Park has affected by the national
conservation policy. This effect is required to national
park’s demarcation and recovery of encroachment.
The Aichi Biodiversity Target (ABT) indicates the
national parks regions using to protect national biodiversity.
According to specific objective of Target 11 of ABT (2010),
every state party augments national parks, but decreases
forest, which as shown in Figure 5. It stated in Chapter 2 of
this thesis earlier that every member country should to
conserve 17% of landscapes and 10% of seascapes areas’
biodiversity associated with operative reserved area-based
protection. There is continued loss of forested habitats in
Bangladesh. In Bangladesh, decrease forest area and
increase loss of biodiversity due different parameters which
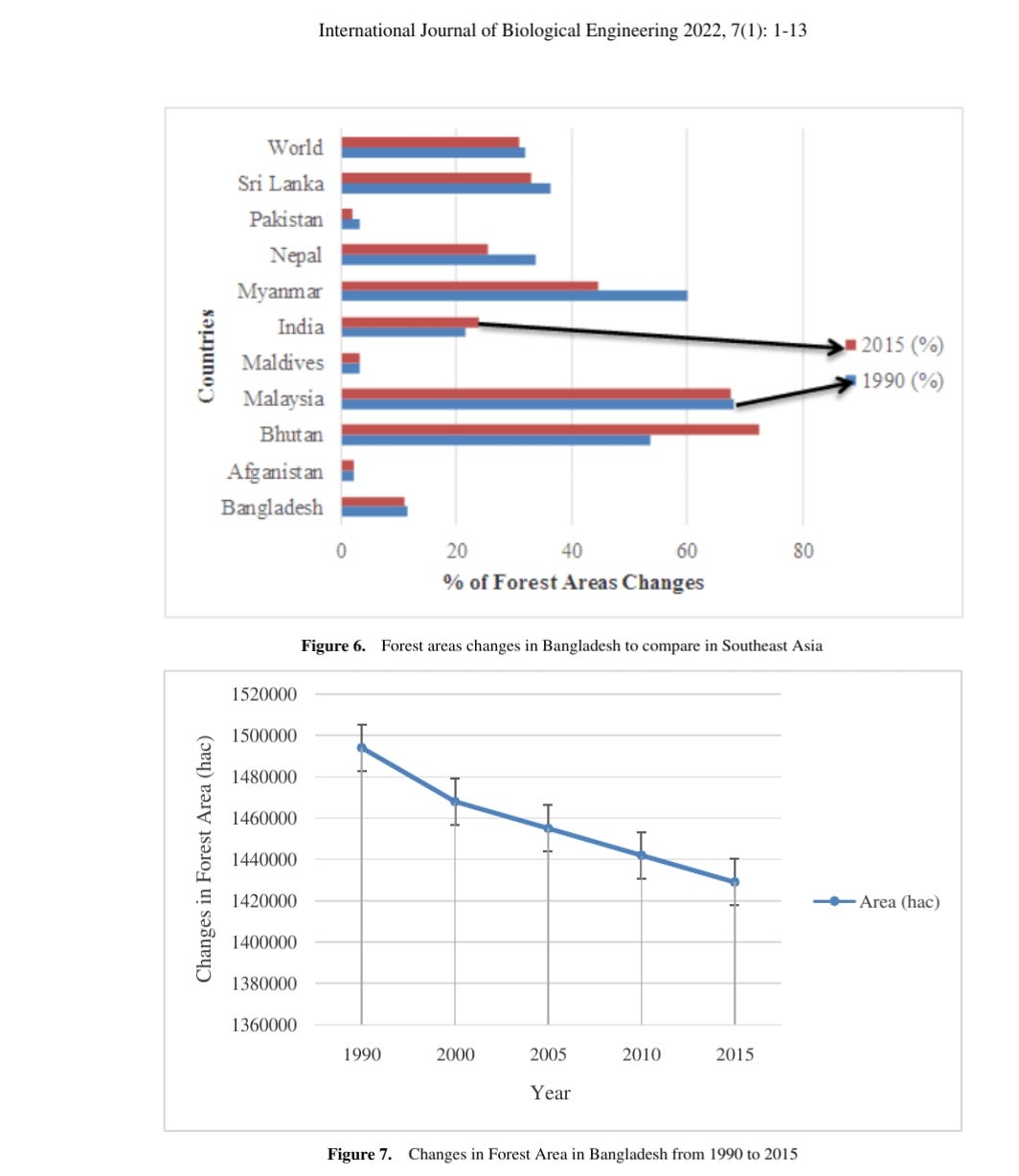
is mentioned earlier. From Figure 6, the study observed that
the percentage of forest area changes is 11.5% in 1990,
and 11.0% in 2015 in Bangladesh [22]. This changes
reflects on the national green economy as well as alarming
on environmental issues. The study also compared with
Malaysia and other countries in south-south-east Asia.
11.50%
11%
10.70%
10.80%
10.90%
11.00%
11.10%
11.20%
11.30%
11.40%
11.50%
11.60%
Forest Area Changes
Forest Area (%)
year
1990
2015
International Journal of Biological Engineering 2022, 7(1): 1-13 7
Figure 6. Forest areas changes in Bangladesh to compare in Southeast Asia
Figure 7. Changes in Forest Area in Bangladesh from 1990 to 2015
From the FAO report, the study illustrated that every year
26,00 ha forest area changes. In 2000, the total forest area
1468,000 ha, in 2005 and 2010, it was 1455,000 ha and
1442,000 ha in Bangladesh respectively. It was changes
tremendously in 2015 as 1429,000 ha. Food and Agriculture
(FAO)-2015 reported a gradual decline in forest area over
the period 1990 to 2015 in Bangladesh. In 1990, the total
forest area of Bangladesh was 1494,000 ha and in 2015 it
became 1429,000 ha, as shown in Figure 7 [23].
Lawachara National Park (LNP) is situated in Sylhet
division, where comprises of evergreen forest and
deciduous forest [28]. From the result of LNP’s biodiversity
survey, it is identified that losses of species diversity of
LNP gradually increased. The study assumed the losses
of biological diversity and environmental dilapidation
unexpectedly in Bangladesh. The losses rate of biological
diversity [4] and bionetworks degradation increase
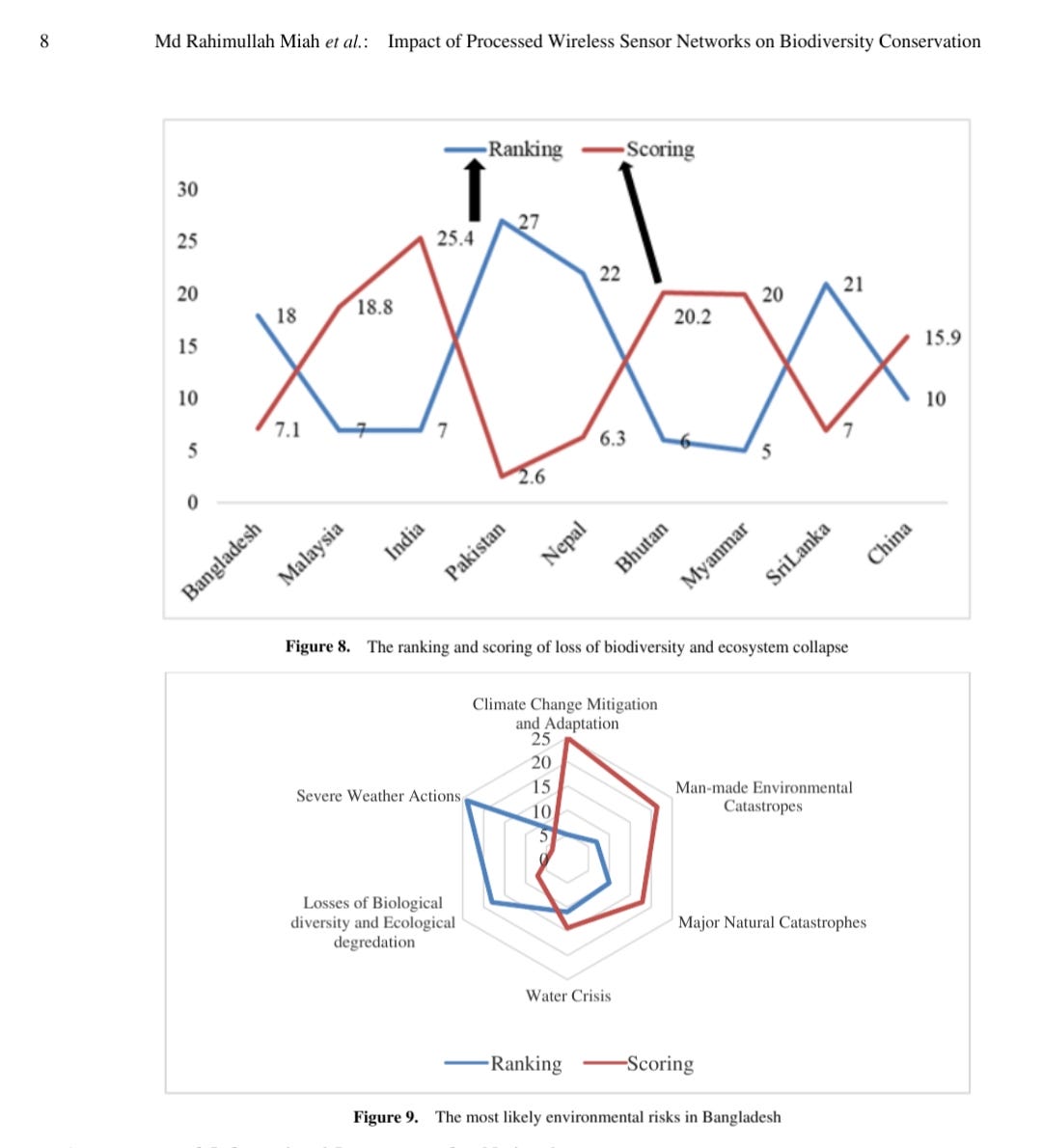
gradually in this country. Figure 8, the scoring study
observed the rank is 7 on favor of scoring 18.8 for Malaysia,
whereas Bangladesh ranking 18 tends to scoring 7.1 [24].
The study indicates the losses of biodiversity, which
influence negative impact in future on biological diversity
and bionetworks services to the upcoming generations of
BD.
1360000
1380000
1400000
1420000
1440000
1460000
1480000
1500000
1520000
1990
2000
2005
2010
2015
Changes in Forest Area (hac)
Year
Area (hac)
8 Md Rahimullah Miah et al.: Impact of Processed Wireless Sensor Networks on Biodiversity Conservation
Figure 8. The ranking and scoring of loss of biodiversity and ecosystem collapse
Figure 9. The most likely environmental risks in Bangladesh
Assessments of Informational Instruments for National
Park’s Biodiversity Conservation are highlighted elaborately
in modern environmental informatics. Human beings live in
the age of information with modernized technology. This
informational instrument enhances the protection, storage,
and sharing of information with rules & regulations to make
a significant facet of economic, cultural and scientific affairs
at scales from local to global [29]. It is clear that Information
Communication and Technology (ICT) has become a
driving force in the area of biodiversity conservation and
the establishment and management of protected areas
[30,31,32,33]. There is a great deal of academic discourse
and debate around theories of the information society
[34] and protected areas. Bangladesh is the most likely
environmental risks, shown as Figure 9.
4. Discussion
The results of this study clearly demonstrate that 'in-situ'
environmental conservation policy instruments are more
appropriate than legal and informational instruments for
biodiversity conservation. There have been limited
comparisons of appropriate legal and informational materials
and conclusions have varied. In this study, the development
of policy declarations produced by national parks and
applications of the Biodiversity Clearing House process were
analyzed as criteria for appropriate biodiversity conservation.
The results of the existing policy instruments are inadequate
in linking national and global perspectives, where there are
some gaps, such as policy formulation, sectoral integration,
declaration of national parks, establishment of digital
0
5
10
15
20
25
Climate Change Mitigation
and Adaptation
Man-made Environmental
Catastropes
Major Natural Catastrophes
Water Crisis
Losses of Biological
diversity and Ecological
degredation
Severe Weather Actions
Ranking
Scoring
International Journal of Biological Engineering 2022, 7(1): 1-13 9
preservation. However, this study includes stakeholder
engagement model development, policy improvement
criteria, and enhanced frameworks for national park
biodiversity conservation and sustainability, priority-based
reasoning models for community-based conservation, and
assessment of the use of updated technologies for
biodiversity conservation. National Park of Bangladesh. The
research indicates the uniqueness of the tools used to
improve national park conservation professionals in the
National Biodiversity Strategic Action Plan through existing
policies and conservation technologies. Engaging with key
stakeholders is essential to dialogue and recognize the
challenges and potential solutions related to national park
biodiversity loss and associated ecosystem service decline
[25]. The research enables the dynamic evidence required
for extensive data transfer and sharing, indexing, online
publication and reporting to effective international
organizations such as CBD in collaboration with Resources
Information Management Systems (RIMS). The study
gathered technical input from stakeholders such as park
managers, biodiversity experts, network officers,
environmental experts, policy-makers, wildlife managers,
educators and relevant organizations, as shown in Figure 10.
Participatory dialogue comprehensive of multiple
stakeholders is crucial to appreciate and discourse different
perspectives and needs [26], and considered many benefits
to policy and technology implementations (e.g., BCHM,
greater legitimacy decisions, higher-quality decisions,
increased compliance) [27]. This type of discussion can also
familiarize stakeholders to potential policy concepts, based
on information from other areas. Finally, the study advocates
a new collaborative approach to drive the stakeholders’
potentiality to further incorporate the information systems
integrating next generations’ biodiversity conservation
perspectives. The study suggested that engagement of
stakeholders enhances the conserving of national park
biodiversity with required policy guidelines.
National Park areas operate with rules and regulations for
promoting and harmonizing of biodiversity policy through
conservation systems, but these rules and regulations are
inadequate due to expansion of insecure advanced wireless
sensor technology towards plants and wildlife. These
systems integrate with Information systems developing
dataset biological diversity Information Systems (BDIS).
The BDIS is a group of tools, which can increase the
competitiveness and gain better information for decision
making with relevant diversity’s system and orders.
Nearly 58% of respondents expressed their opinions for
development of BDIS for Lawachara National Park [8],
which connects with geospatial technology, biodiversity
clearing house mechanisms, IOBIS and modern conservation
technology. But till to date, there is no effective Park Area
Management Control Unit (PAMCU) including biodiversity
database, clearing house mechanisms (CHM), visitor’s
database as well as information systems in developing
countries and other local places. The study represents
alarming on environmental diseases like tracheal disorder
and cancer, coronavirus disease, onset acute respiratory
distress syndrome (ARDS), sudden cardiac arrest, sudden
numbness, neurofibromatosis, stomach cancer, liver
cirrhosis, falling down, fever, dermal diseases (like tinea
corporis, erythema gyratum repens, contact dermatitis) etc.
due to misuse of wireless sensor devices with clouding
networking system [15,17,35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42,43,44,
45]. Furthermore, man-made technological climate crisis,
heatwave, flash flood, wildfire, landslide occur due to
tracking with wireless sensor technology [10,12,15,16].
Figure 10. Stakeholder Engagement on National Park Biodiversity
10 Md Rahimullah Miah et al.: Impact of Processed Wireless Sensor Networks on Biodiversity Conservation
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, the study evaluates three of the four types
of conservation instruments of the Convention on Biological
Diversity. These are legal, in-situ and informational
instruments for developing countries including National
Parks (NP) – as a study site. Based on these instruments,
national parks are not well managed based on the
effectiveness of national park management and the
prioritization of political commitment to biodiversity
conservation. However, this study attempts to develop a
complete scenario of under-management factors in
conserving NP biodiversity in developing country. The
findings of this study clearly indicate that any national park
database is an important resource in relation to traditional
forest policy, misuse of advanced wireless sensor technology,
illegal logging, wildlife poaching, collection of NTFPs,
parkland encroachment, invasive alien species and
biodiversity clearing house process for loss of biodiversity in
national parks. The results of this study support the adoption
of environmental conservation policy instruments linking
with secure wireless sensor technology that create National
Park Biodiversity Protection worldwide.
6. Declaration
Funding
This research work is a part of ISNA Experiment of the
PhD Thesis, which was funded by the Zamalah Postgraduate
Scholarship of UNIMAS, Malaysia and also sponsored by
the Information and Communication Technology Division,
Ministry of Posts, Telecommunication and Information
Technology, Government of People’s Republic of
Bangladesh. The funders had no role in the design of the
research, in data collection, analyses or final interpretation of
data, in the writings of the manuscript, or in the decision to
publish the findings.
Data Availability
The data being used to support the findings of this research
work are available from the corresponding author upon
request.
Competing Interests
The authors declare no potential conflict of interests in this
research work. Thanks for all that you do to stop this biohack on all that is natural and made in the image of GOD and may Romans 8:31 be our guiding light.






No comments:
Post a Comment